Caudal Occipital Malformation Syndrome – COMS
Etiology Phenotypic selection has led to variability in canine skull shape. The brachycephalic phenotype was selected initially for its strong bite force. Later, breeds with round heads and foreshortened noses were desired because their facial... Read More
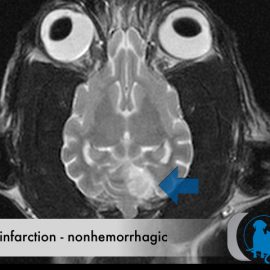
Brain Infarction – Nonhemorrhagic
Etiology Nonhemorrhagic infarctions, otherwise called ischemic infarctions, are the result of the acute interruption of blood flow to an area within the brain. The usual cause for a nonhemorrhagic infarction is the occlusion of an... Read More
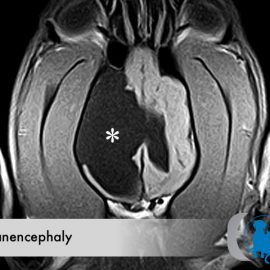
Hydranencephaly
Etiology Hydranencephaly is a congenital malformation of the brain in which the cerebral hemisphere(s) are absent to varying degrees. Hydranencephaly is an extreme form of porencephaly, a condition in which large cystic regions develop within the... Read More
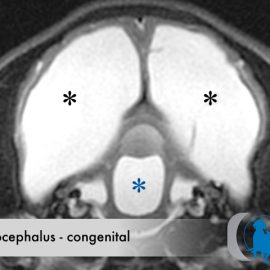
Hydrocephalus – Congenital
EtiologyThe term hydrocephalus is derived from the greek "hydro" for water and "cephalus" for head. As such the condition is one in which there is an increased accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) within the intracranial... Read More