What is MRI?
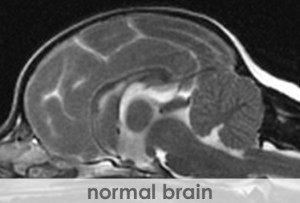
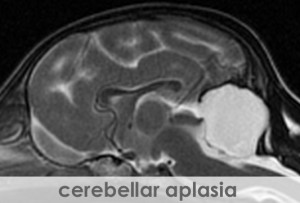
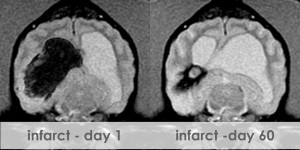
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a sophisticated computerized imaging technique, which has been a clinical diagnostic tool since 1980. MRI is used to create images with extraordinary detail of the body or brain by applying nuclear magnetic resonance phenomena. The distribution of hydrogen nuclei (protons), found in cellular water, depends on the tissue type and whether or not the tissue is healthy or diseased. MRI measures and records changes in the magnetic properties of these protons. The MRI technique uses a strong magnetic field, pulsed electromagnetic fields known as gradients, and radio waves to excite the protons and produce the image in the region of interest. The image is produced then displayed on a gray scale from black to bright white. The image brightness is a complex function of the hydrogen concentration or intensity. Contrast, described as the difference between signal intensities, provides the optimum difference between light and dark regions of the tissue or organ to help the veterinarian detect lesions, such as a tumor. Although MRI is normally a noninvasive technique, contrast agents can be administered to a patient to enhance a region of interest.
How is MRI used?
Soft tissue, such as internal organs, is relatively transparent to X-rays, limiting the practical application of other imaging modalities such as computed tomography (CT). MRI, however, has excellent sensitivity for these tissues with 100% increase in soft tissue resolution compared to it's closest competitor CT. MRI has the additional benefit of not using ionizing radiation. The magnetic resonance phenomenon has been steadily gaining in vitro application in the fields of chemistry, biochemistry, and the medical life sciences since its inception in 1946. The technique was first extended to a live animal by Jasper Jackson in 1967, and the first two-dimensional MR image was generated in 1972 by Paul Lauterbur. Since initial reports of the identification of central nervous system (CNS) abnormalities by magnetic resonance imaging during the 1980's, the progression of MR as a diagnostic modality for CNS disease has been rapid. Magnetic Resonance Imaging became routine in human medicine during the 1980s. The superior clarity of the images, particularly of the brain, combined with its non invasive nature led to its quick acceptance.
MRI in Veterinary Medicine.
Until recently MRI has had limited application in veterinary medicine, primarily due to the expense of the imaging unit and associated computer needs, as well as the requirement for specially constructed rooms to house the units. However, a few specialty veterinary facilities including Advanced Veterinary Medical Imaging have obtained their own imaging units for veterinary use. Most veterinary facilities rely on older, used equipment. Our new, state of the art, high field GE MRI scanner will ensure a more efficient and rapid exam. Furthermore the most sophisticated monitoring equipment available, will minimize anesthetic related concerns. Advanced Veterinary Medical Imaging has acquired the most dedicated and skilled staff available in the MRI industry today in an effort to provide the best care possible for your pet.